When it comes to using a backup power option the choice is usually between a solar battery or a generator. During outages it is often important to have a backup solution to power a home or business. Both solutions have advantages and disadvantages. In order to understand which backup power solution might be best for you we guide you through the differences between solar battery backup and generators in terms of cost, convenience, performance and environmental impact.

What is Meant By a Backup Power Solution?
A backup power solution refers to a system designed to provide electricity to a home when the main power grid fails. Severe weather and natural events can cause power outages and surges resulting in a loss of power to a home or business. A backup power solution like a solar battery or generator is designed to keep the lights on and appliances working while the main power is down.
What is a Solar Battery?
A solar battery is an energy storage device that is connected to a solar system, storing electricity to be used at a later date. A backup system like a solar battery is used when solar panels do not produce enough energy like during a power outage, on cloudy days or during the evening. A solar system captures the sunlight and converts it to energy to be used in the home. However the energy can only be used when the solar system is working during sunlight hours and any excess energy is usually returned to the grid. A solar battery stores the surplus energy created by the solar panels and continues to supply it to the home.

Image Credit: Sofar
Types of Solar Battery Systems for Backup Power
Solar batteries have significantly evolved over the years from the original widely used lead acid designs to the current lithium-ion technology. While lithium-ion batteries are the most common battery system, the three other types – lead-acid, nickel cadmium and flow, are still used.
- Lithium-ion batteries: Lithium-ion batteries are the most popular choice for solar batteries in residential and commercial installations. They are the newest technology, require very little maintenance, are lighter, and don’t take up much space compared to other battery types. The average 10 kW lithium-ion battery will typically weigh between 89kg and 132kg, while the same size lead acid battery is between 132.5kg and 300kg. Lithium-ion batteries are more expensive than others on the market. However, their upfront cost is often offset by their longer lifespan, higher energy density and greater efficiency.
- Lead acid batteries: Lead acid batteries for solar storage are called deep cycle batteries. They are one of the original types of solar batteries with technology dating back 160 years. Lead acid batteries have always been robust and reliable however, they are very heavy and can tend to take up a lot of space. They have a high power discharge but low energy and can take up to 14 hours to fully charge. Lead acid batteries do cost less so are still very popular for those looking for savings.
- Nickel cadmium batteries: These types of batteries are not often used in residential but commonly used for some large scale operations. Nickel cadmium batteries are extremely durable and can operate in high temperatures. They have a long lifespan and are preferred over lithium-ion batteries in situations that demand consistent and uninterrupted power output.
- Flow batteries: Flow batteries are one of the newest technologies and contain water-based electrolytes flowing between two chambers in the battery. They have a longer lifespan than lithium-ion batteries and are suitable for extended hours of operation. As they are quite new to the market and expensive in comparison, they are not as popular as lithium-ion in the residential and commercial sector. Flow batteries are more likely to be used in large installations instead of residential because they are prone to low power density.
Understanding Solar Batteries as a Backup Power Solution
Solar batteries are a backup power solution that stores excess energy created by solar panels and uses it for lights and powering appliances. Solar batteries provide clean energy when you need it most with a range of features including:
- Environmentally friendly: Solar batteries are powered by green energy and have no impact on the environment. The process of storing energy produces no harmful emissions or waste byproducts.
- Cost savings: Solar batteries store the excess energy created during the day to be used in the evening. This places less reliance on the grid and purchasing electricity from a provider, keeping costs down on energy bills.
- Energy independence: With the combination of solar panels and a solar battery, homeowners are able to rely less on the grid and become energy independent. With a solar battery storing the surplus energy that is created during the day, a home can be powered completely without reliance on the electricity grid.
- Quiet operation: Solar batteries operate quietly unlike other battery backup solutions. They are quiet because they have no moving parts and, instead, rely on chemical reactions which are inherently quiet to store energy.
- Long term investment: Solar batteries offer long term environmental and financial benefits, making them a worthwhile investment. Despite the initial costs, solar panels and solar batteries will save money on electricity bills, help the environment and even increase the value of a home.
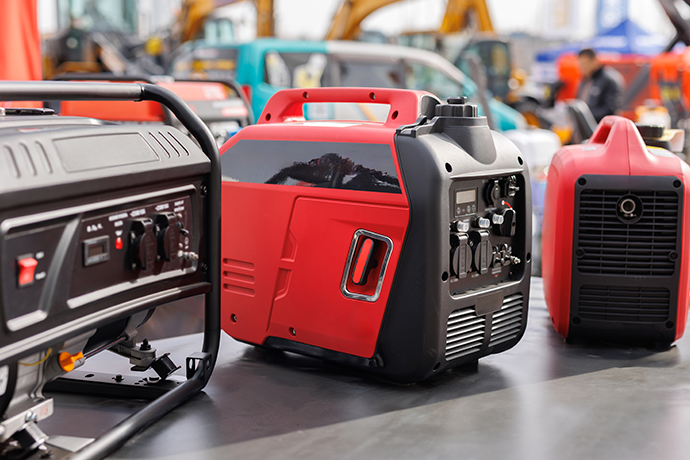
What is a Generator?
A generator is a unit that connects to the home’s electrical panel and kicks in when the power goes out. Generators produce energy by burning fuel and is the more traditional backup power most people would be familiar with. Using fuels like gasoline, diesel, or natural gas, generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The generator is connected to the house via a transfer switch which is an electrical device installed next to the electrical panel in a home. Unlike a solar battery, generators do not rely on stored energy created by solar panels but rather make their own electricity internally. The average whole house generator is usually between 15,000 watts and 20,000 watts, depending on the power consumption of the home. A 20,000 watt generator weighs from 690kg to 1023 kg, and measures approximately 210-220 cm in length, 80-100 cm in width, and 110-130 cm in height.

Types of Generators for Backup Power
There are two main types of generators for backup power – portable and standby (whole house) generators. Both will provide backup power so the choice is dependent on personal requirements.
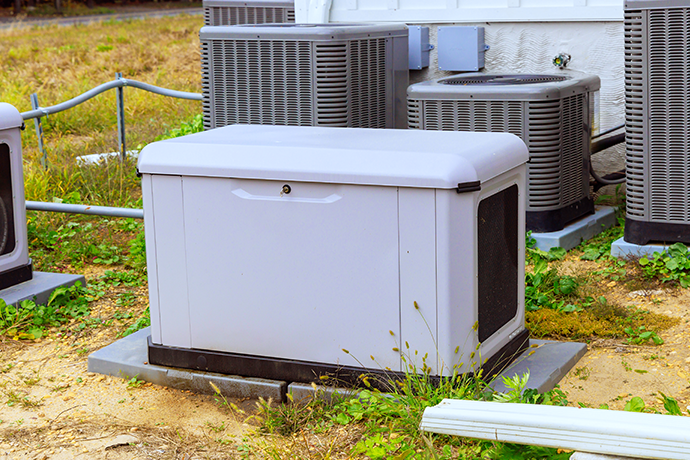
- Whole house generators: This is a permanently installed generator that will automatically switch on when the power goes out and provide consistent electricity to the entire home. Whole house generators are installed outside the home usually on a cement slab and are permanent fixtures. Whole house generators are connected to the home’s electricity supply via a transfer switch. When installed, they must have clearance from doors, windows and vents to prevent fumes from entering the home. Whole house generators are usually quite large and heavy and require a large space for installation.
- Portable generators: A portable generator is a mobile power source that can be set up for backup power in the event of a disruption. These generators are typically much smaller than whole house generators and only used to power essential appliances and lights for a temporary time period. Portable generators would usually be about 7,000 to 10,000 watts for temporary backup power and are often run on diesel fuel.
Understanding Generators as a Backup Power Solution
Both whole home and portable generators are a traditional backup power solution to provide electricity during power outages. Despite their older technology, they are still quite popular as power sources. Features of generators as backup power solutions include:
- Immediate power: Generators provide immediate power as soon as a power outage is detected. They are a reliable source of backup power, ensuring appliances and lights remain operational.
- Fuel availability: The dependence on the availability of fuel can be an issue. In the event of a power outage, fuel like diesel may be in high demand and thus less available, reducing the backup power capability. Gas is a more readily available fuel but burns quickly requiring regular refilling.
- Low initial cost: Generators are usually less expensive to purchase compared to battery backup systems. However, the running costs with fuel expenses are more expensive.
- High power output: Generators deliver a high power output, making them ideal for backup power for whole houses and those with large energy requirements.
- Noise and emissions: Unlike battery backup systems, generators are loud and can produce emissions. Diesel generators, in particular, are known for their noise and environmental pollution.
Comparing Solar Batteries to Generators
To understand the difference between solar batteries and generators, it is important to compare the key factors. Solar batteries and generators each have their advantages and disadvantages and the right one for you will depend on your individual needs, priorities and budget. When comparing solar batteries to generators, the main considerations include cost, environmental impact, maintenance, noise and emissions, power output, and reliability.
Cost
- Solar batteries – Solar batteries have a higher initial cost than generators but less expensive ongoing costs and maintenance. The average solar battery costs between $8,000 and $15,000, but this can be offset by the significant savings in energy bills.
- Generators – The upfront cost for generators is much less than solar batteries but the ongoing costs are more. The average generator costs around $2,000 for portable, and up to $10,000 for a permanent whole house generator. Ongoing costs include paying for fuel and regular maintenance.
Government incentives
- Solar batteries – Government incentives are available for solar batteries. The Cheaper Home Batteries Program provides a 30% discount on the upfront cost of installing eligible small-scale batteries as part of the expansion of the Small Scale Renewable Energy Scheme.
- Generators – There are no Government incentives or rebates for purchasing, installing or using generators.
Environmental impact
- Solar batteries – Solar panels are a renewable energy that rely on the sun to create electricity. They are environmentally friendly.
- Generators – Generators rely on fossil fuels to produce electricity. They are not environmentally friendly and produce carbon omissions that are bad for the environment.
Maintenance
- Solar batteries – Solar batteries require very little maintenance compared to generators. Solar batteries just need occasional checks and software updates. They are designed for long-term worry free operation.
- Generators – Generators require regular maintenance because of their mechanical parts and use of fuel. To function properly, generators need maintenance and servicing every 6 to 12 months.
Noise and emissions
- Solar batteries – Solar batteries operate silently and have no emissions.
- Generators – Generators are loud and produce exhaust fumes.
Power output
- Solar batteries – Power output is the rate that electricity can be delivered. Solar batteries are primarily used for electricity storage but do not always have as high a power output as generators because they rely on the sunshine for electricity.
- Generators – Generators have an extremely high power output and are designed to deliver a higher wattage than solar batteries. Their power output is guaranteed as generators rely on fossil fuels to create electricity.
How to Choose between Solar Battery and Generator for Backup
Choosing the best backup power solution will depend on your needs and circumstances. Consider these factors when choosing between solar battery and generators for backup power.
- Power required: Assess your power requirements to see if solar batteries or generators will better suit your needs. For most residential and commercial applications, solar is the best choice. However, generators can still be a reliable power source in the event of a power outage.
- Budget: Consider the initial cost while taking into account ongoing costs and maintenance requirements.
- Environmental concerns: Evaluate how important the environment is in your choice. If you prioritise sustainability and reducing the carbon footprint, solar batteries and a solar system are by far the best choice.
- Noise sensitivity: If noise pollution is a concern, solar batteries are silent as compared to generators that are quite loud.
- Solar panels already installed: If you have solar panels installed already, a solar battery is going to be the best option for backup power.
The main backup power solution is a choice between a solar battery and a generator. While generators are the original backup power solution, the renewable resource of solar panels and solar batteries provides a plethora of benefits. To help you determine the best solution for your home, our article explains the difference between solar batteries and generators. For further information about solar batteries contact the team at Tasmanian Safer Solar.