Solar panels work by converting the sunlight to electrical energy, which is used to run appliances in the home rather than use electricity from the grid. Solar panels can be found in residential buildings on rooftops powering a single household, through large solar farms that power many on the grid. Despite the difference in application, they work the exact same way no matter the size. Understanding how solar panels work can help you decide if you should have them installed. For those that already have solar panels, it can help you identify if they are working to their maximum capacity. In this article we will guide you through what solar energy is, what solar panels are and how they work together to create electricity.

What Is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is the energy that is derived from the radiation of the sun. It is produced by a process called nuclear fusion that takes place in the sun. When nuclear fusion occurs in the sun, it converts hydrogen to helium and produces massive amounts of energy which is perceived as sunlight and heat.
What Are Solar Panels?
Solar panels are devices made from a semiconductor material like silicon that is installed in a metal panel and frame within a glass casing. These panels contain photovoltaic (PV) cells, known as solar cells, that convert the sunlight to DC electricity. A solar panel system is made up of multiple solar panels and an inverter, and are usually fitted on a roof for residential or commercial purposes to produce electricity.
How Do Solar Panels Convert Solar Energy To Electricity?
Solar panels are made up of photovoltaic cells (solar cells) constructed with a positive and negative layer that create an electric field like a battery. When the sun shines, it contains photons (tiny particles of electromagnetic energy). These particles connect with the solar cells and knock the electrons loose from their atoms. These loose electrons are then captured so they move in the same direction around the circuit which then forms a direct current (DC). This direct electrical current is then fed into a solar inverter and converted into AC (alternating current) power, which is sent to your electrical meter to be used to power various appliances and devices in your home.
What Does A Solar Inverter Do?
A solar inverter is a piece of electrical equipment that converts the generated energy collected from the solar panels into electrical energy that can be used to power appliances. In other words, it is the component that converts the direct current (DC) created in the solar panel to alternating current (AC) that can be used in the home. Without an inverter you wouldn’t be able to use the power from your solar panels to run your household devices as devices and appliances require alternating current to operate.

The solar inverter takes the DC power and runs it through a transistor, which then releases AC power as the output.
It does this by switching on and off quickly at around 3000 times a minute. This rapid switching creates a pulse of current that alternates between positive and negative and disrupts the linear flow. Inductors and capacitors in the inverter then regulate and stabilise the energy to form a sinusoidal wave which is the most common type of AC. Once the AC is produced, the energy is then sent into the home.
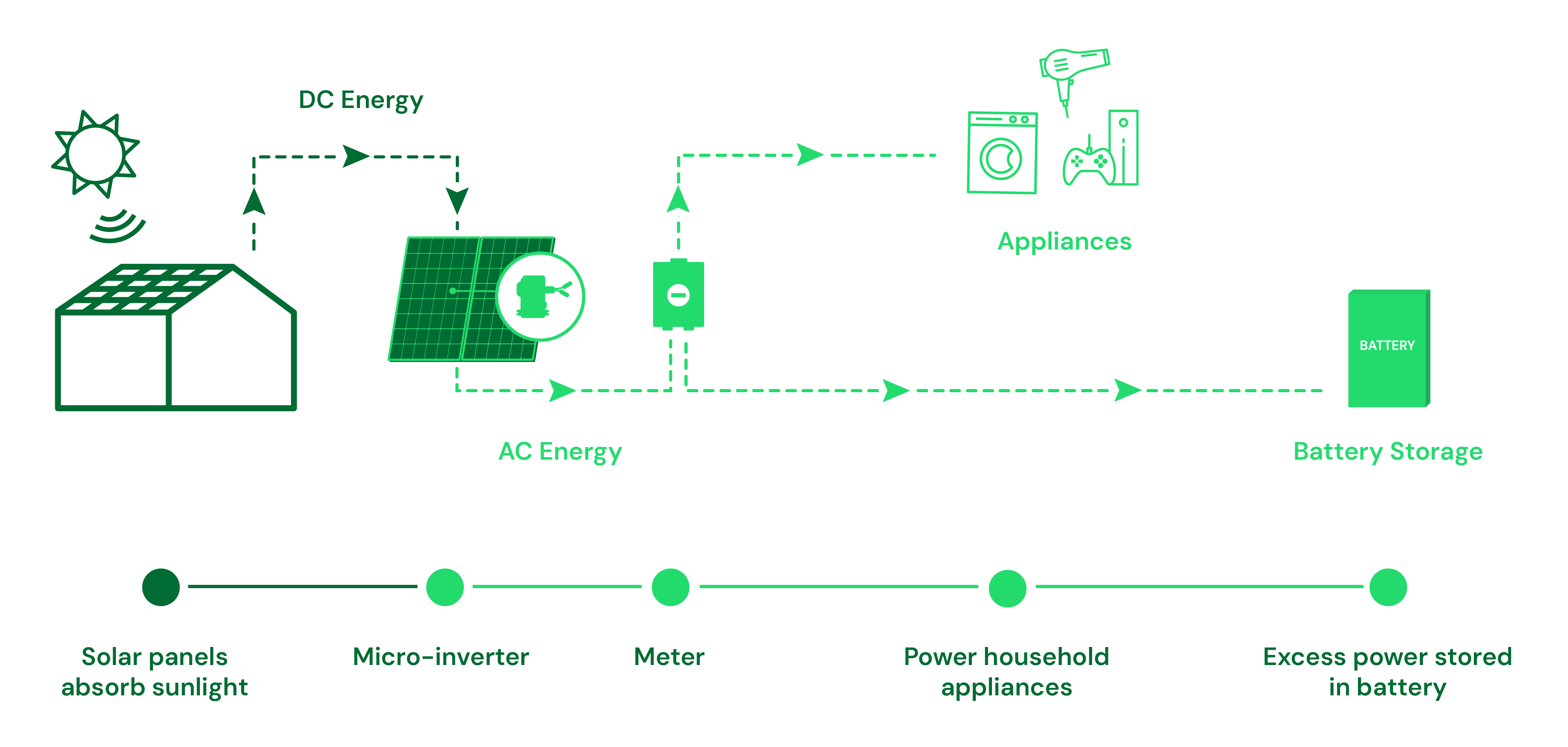
How A Solar Panel System Works
When sunlight hits the solar panels, the photovoltaic cells convert it to electricity. Let’s take a look at how a solar panel system works to turn the sun’s energy into electrical power.
- Sunshine hits the solar panels: When solar panels are installed on your roof, they are positioned in a way to receive the maximum amount of sunlight. When the sun shines, the solar energy hits the solar panels and the photovoltaic cells absorb the light energy.
- Photovoltaic effect: The photovoltaic cells in the solar panels absorb the sunlight and create direct current. These photovoltaic cells are basically a double layer made up of two pieces of semi conducting material like silicon. When the sunlight strikes the cells, it causes the electrons to move which creates the flow of direct current.
- Conversion to alternating current: The direct current is sent to the inverter, which then converts it to alternating current to be used in the home.
- Electricity distributed: The alternating current electricity is sent from the inverter to the electrical panel called a breaker box. The main breaker box is the service panel that makes it possible to distribute the electricity throughout the home.
- Electricity is supplied to home: The electricity generated by the sun is supplied to the home to power lights, appliances and electronic devices.
- Net metering and grid connection: If your solar system is producing excess power (more than you can use in a day), it can be sent back to the grid through the net metering system. This meter records the amount of energy you are using as well as how much is being sent back to the grid.
- Optional solar battery storage: If you want to use all of your solar energy, rather than send it back to the grid, you can invest in a solar battery. When added to your solar system, a solar battery stores excess electricity generated by the solar panels. Solar batteries allow you to use excess energy during the night time, on cloudy days and when your solar system is not producing much electricity.
Understanding how solar panels work is a good step towards deciding if solar panels are right for you. In this article, we have discussed what solar energy is, how they convert sunshine to electricity, and the process of how solar panels work. For further information about solar panels, contact the team at Tasmanian Safer Solar.