All solar panels are designed to convert sunlight into electricity, however there are different types of solar panels on the market. In Australia, the three main types of solar panels are monocrystalline, polycrystalline and thin film, each with different durability, efficiency and cost advantages. Whether you are installing solar panels for the first time, replacing or upgrading your old ones, it is important to make an informed decision on what is available. With a good understanding of the different types of solar panels, their cost, efficiency and durability, you can choose the best panels to suit your energy needs. Read on to discover how solar panels work, the main types of solar panels, pros and cons and what to consider when choosing a solar panel type.
How Solar Panels Work
Solar panels work by taking the sun’s energy and transforming it into electrical energy for a home or business. A typical solar panel is made up of individual solar cells that are usually made from silicon. These cells, also known as photovoltaic cells, are installed within a metal panel frame with a glass casing. When the sunlight connects to the solar panel, it is absorbed by the photovoltaic cells and converted to direct current (DC) electricity. This direct current is then fed into the solar inverter which converts it into alternating current (AC) electricity to be used to power appliances and devices in the home or business.
Main Types of Solar Panels
The three main types of solar panels are monocrystalline, polycrystalline and thin film. Each uses a unique solar cell technology which is the main differentiator. They all have different benefits, disadvantages and characteristics that make them better for some applications rather than others. To understand how each solar panel is different, take into account their cell technology, efficiency, materials and power output.
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
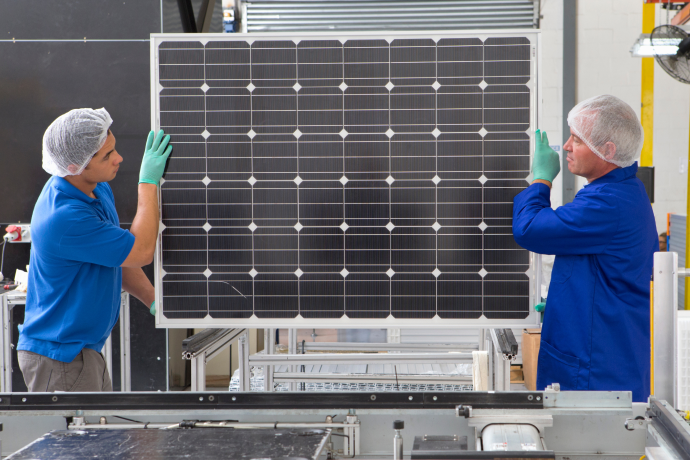

Monocrystalline solar panels are a photovoltaic panel made from a single continuous crystal structure, hence their name. They are constructed by growing a large single crystal of high purity silicon and slicing it into thin wafers. The wafers are assembled to make up the solar cells in the panel. Monocrystalline panels are often considered the most efficient type of solar panel on the market with 20 to 25% efficiency and a lifespan of 25 to 40 years.
Material
The materials in monocrystalline solar panels are:
- Silicon: Solar cells in monocrystalline panels are made from pure silicon crystal sliced into wafers.
- Alumiumium: The frame the solar panels sit in is made of aluminium.
- Glass: Tempered glass on the front of the solar panels protects the cells from the elements.
- Vinyl backsheet: This vinyl material encapsulates the side and back of the solar panel, protecting it from moisture and heat.
Cost
Monocrystalline are one of the more expensive solar panel types because of their manufacturing process. On average, a monocrystalline solar panel costs about $1.50 to $2.50 per watt.
Rated power output
The rated power output (amount of electricity it can generate in standard test conditions) of monocrystalline solar panels is about 500 watts. However some of these types of panels can exceed 600 watts.
Efficiency
Efficiency is a measure of the panel’s ability to convert sunshine to electricity. The efficiency of monocrystalline solar panels is 17 to 24%.
Pros and cons of Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Pros
- High efficiency
- Long lasting
- Conserve space
- Easy to install
Cons
- More expensive
- Complex manufacturing process
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
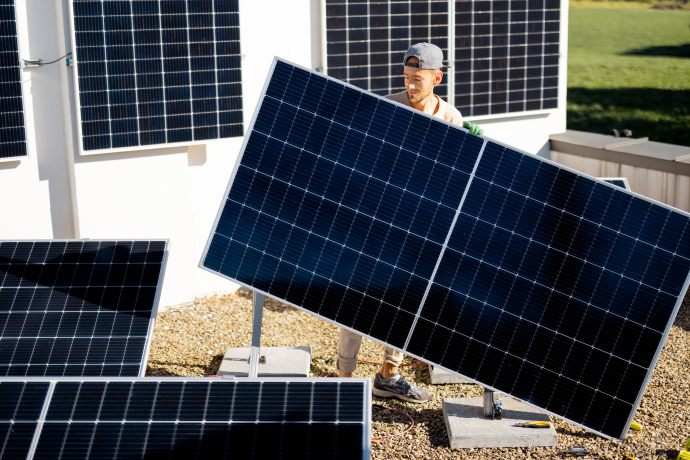

Polycrystalline solar panels are made of multiple pieces of silicon blended together and then sliced into wafers. They are constructed by melting together multiple silicon crystals and pouring them into a mold. The large cubic silicon ingot is then sliced into wafers of thin, square sheets. The multiple silicon crystals within a polycrystalline panel reflect the light which gives this type of panel its blue hue. The energy efficiency of polycrystalline solar panels is approximately 15 to 17% and lifespan is 25 to 40 years.
Material
The materials in polycrystalline solar panels are:
- Silicon: Multiple fragments of silicon crystals melted together and sliced into wafers
- Alumiumium: The frame the solar panels sit in is made of aluminium.
- Glass: Tempered glass on the front of the solar panels protects the cells from the elements.
- Vinyl backsheet: This vinyl material encapsulates the side and back of the solar panel, protecting it from moisture and heat.
Cost
Polycrystalline solar panels are slightly less expensive than their monocrystalline counterparts. The average cost is about $1.20 to $2.00 per watt.
Rated power output
The rated power output of polycrystalline panels is about 240 to 300 watts.
Efficiency
The efficiency of polycrystalline solar panels is 15 to 17%
Pros and cons of Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Pros
- Lower upfront cost
- Durability
- Less complex manufacturing process
Cons
- Lower efficiency rates
- Less power per square metre
- Lower heat tolerance
Thin film Solar Panels

Thin-film solar panels are a type of photovoltaic solar panel that is made up of thin film solar cells. These thin layers of photovoltaic materials convert the sunlight to electricity. They can be over 300 times thinner than a traditional silicon solar panel and are applied to substrates like plastic or glass. While they are thin, which is ideal for limited spaces, they do not operate as well as crystalline solar panels and have a limited efficiency of about 6 to 18% and lifespan of 10 to 20 years.
Material
The materials in thin film solar panels are:
- Silicon: Amorphous silicon is a non crystalline form of silicon that is flexible and light weight.
- Cadmium Telluride: Another potential material used in thin film cells that is effective at absorbing light.
- Copper Indium Gallium Selenide: A material sometimes used in thin film cells for its excellent performance in low light conditions.
- Backing materials: Glass, plastic or metal on which the thin film layers are deposited.
Cost
The average cost per watt for thin film solar panels is between $1.00 and $1.80.
Rated power output
The rated power output of thin film solar panels is between 100 watts and 400 watts.
Efficiency
Thin film solar panels are not the most efficient with a range of 6 to 18%. However, they are ideal for diverse applications like curved surfaces.
Pros and cons of Thin Film Solar Panels
Pros
- Flexible, lightweight design
- Low cost
- Sleek, thin appearance
Cons
- Low efficiency
- Short lifespan
- Space requirements
- Durability issues
What To Consider When Choosing a Solar Panel Type
When choosing the right type of solar panel for your needs, take into account panel features and your own personal circumstances.
Solar Panel Features
Temperature coefficient
The temperature coefficient is crucial when considering which solar panel type to invest in. It is the measurement of how much a panel’s power output decreases with every celsius degree raised over the optimal temperature which is usually 25°C. If a temperature coefficient is low that is a good sign that the solar panel can withstand hot conditions. If installing a system in a warmer climate, the temperature coefficient is essential to gauge if the system will be able to perform well and offer maximum savings. You may want to consider a solar panel with the lowest possible temperature coefficient like a monocrystalline pane in these conditions. For those in cooler climates, the temperature coefficient is less important as the impact of heat related loss is minimal.
Durability and lifespan
The solar panel’s ability to withstand significant stress is known as its durability. This factor should be considered particularly if you live in areas with regular storms, like hail and wind. You will need to choose a solar panel that is resilient against the environmental conditions with strong materials like tempered glass. Most solar panels have an operational lifespan of about 25 to 30 years, however some will last less or longer than that time. The lifespan of a solar panel will impact your return on investment and the amount of time before you may need to consider replacement. If you choose a lower quality solar panel it is likely that the lifespan will be less and degradation will occur at a faster rate.
Personal Considerations
Power consumption
When taking into account your power consumption, it will impact the type and size of solar panels you may need. In order to have a well performing solar system it needs to be able to produce the amount of electricity you require. When trying to work out what size and type of system you need, go to the online calculator for an estimate. Using data from the Bureau of Meteorology, this calculator can estimate potential savings and recommend solar system type and size.
Budget
While budget is important when choosing solar panels, remember the cheaper solar panels may not be as efficient and reduce long term savings. Take into account the budget but keep in mind there are government rebates and incentives to help with solar system prices.
Roof size
The size of your roof does have an impact on how many solar panels you can install. If your roof has limited space, you may need to purchase higher efficiency solar panels.
Which Solar Panel is the Best Choice for You?
When to Choose Monocrystalline Solar Panels
If you need to maximise electricity generation in a limited space, you should consider monocrystalline solar panels. They are physically smaller compared to other panels but have the highest efficiency rating per square metre. They also have the bonus of an extended lifespan and warranty. Monocrystalline panels have sleek design that blends in well with rooflines so has aesthetic appeal. Although more expensive than other solar panels, these are excellent for those who want to harness a significant amount of electricity in a small space.
When to Choose Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Should price be a major consideration, polycrystalline panels are a mid level option that costs less but still delivers the efficiency and durability required. For those wanting to enter the solar system industry on a budget, polycrystalline panels are ideal and you will save more money in the long run.
When to Choose Thin Film Solar Panels
Thin film solar panels are less energy efficient or powerful than other types but they are the most flexible and can be used for a myriad of applications. If you have a caravan, tiny home or a roof that does not have a flat or stable surface, thin film panels are the answer. They are also extremely lightweight which makes them ideal for buildings without a strong roof.
With so many solar panels and types on the market, it can be difficult to distinguish which is the best for your purposes. Our guide to the different types of solar panels explains the different solar technologies and how they impact efficiency and performance, the pros and cons of each and how to choose the right solar panel type. For further information contact the experts in solar panels at Tasmanian Safer Solar.