Switching entirely to solar energy is becoming an increasingly attractive option. Off-grid solar systems, in particular, are gaining popularity across Tasmania, enabling residents to fully disconnect from the electricity grid. According to the latest trends from the Clean Energy Council, off-grid solar installations have risen by 47% since 2024. Residents who make the switch can enjoy a range of benefits, including a reduced carbon footprint, zero electricity bills, and reliable access to energy in remote or isolated communities. Although they will require greater upfront costs. Read on to find out everything you need to know about installing an off-grid solar system.

What is an Off-Grid Solar System?
Off-grid solar refers to a system in which you are completely disconnected from the main electricity grid. This allows you to be self-sufficient, in which you are completely reliant on generating energy through your solar system to meet your household’s power needs.
Off-grid solar systems have grown in popularity as a way to generate your power and eliminate energy bills. They are also a great way for rural or isolated communities with limited access to electricity infrastructure to generate and power their homes entirely on their own.
Components of an Off-Grid Solar System
An off-grid solar system comprises several essential components. These include:
- Solar Panels
The central component of any solar system. These are the devices that capture sunlight and convert it into DC (Direct Current) electricity. Your capacity, or number of solar panels, will depend on your energy consumption and the amount of sunlight in your area. - Solar Batteries
Batteries are vitally important to the success of going off-grid. These are the devices that store all of the excess energy your panels create. This allows you to use your home appliances when you’re not generating solar energy for a continuous supply, in particular at night. - Solar Inverters
Devices that convert your DC (Direct Current) solar electricity from your panels and battery into AC (Alternating Current) electricity, which is the type used to power your home. - Solar Charge Controller
Essential for the effectiveness of both your solar panels and batteries. A Solar Charge Controller regulates the rate at which an electric current is added to or drawn from your batteries to avoid any overcharging. Helps to maintain your battery’s lifespan and ensure the overall efficiency and safety of your off-grid system. - Backup energy source
On occasion, your solar system may not be enough to meet your energy needs. In these instances, it’s important to consider a backup energy source, such as a generator. These devices are typically fueled by diesel, propane, or natural gas to provide secondary power.
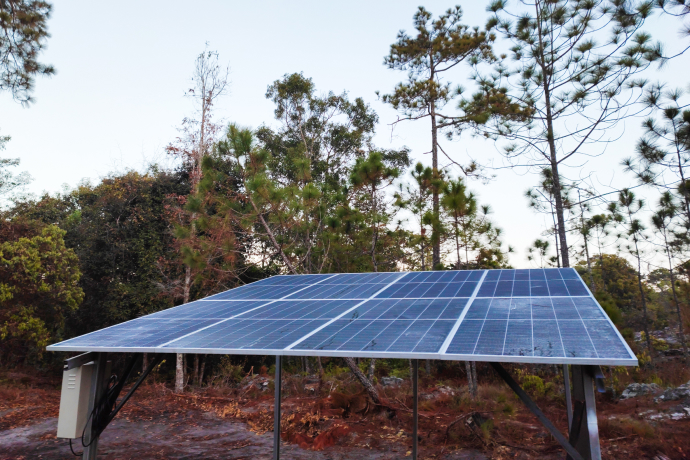

How Does Off-Grid Solar Work?
An off-grid solar system will typically work through the following steps:
- Energy Capture – Solar panels absorb the sunlight to produce DC electricity
- Charge Controller – Your charge controller manages the flow of electricity from your solar panels to your battery or inverter
- Filling Your Battery – Your battery stores all of the excess electricity from your solar panels. This will allow you to use energy when the sun isn’t shining.
- Inverter – Your inverter converts the DC energy from your solar panels or batteries to AC to power your home.
- Backup Power – As a last resort, you may need to power your home using a backup generator, often during periods where solar energy is more difficult to harness (excessive cloud) or during high energy demands for your home.
Types of Off-Grid Solar Systems
If you’re debating whether to invest in an off-grid system, you must consider the different options for installation. These will include:
- DC Solar System
In a DC-coupled system, the DC energy generated by your solar panels is sent directly to your battery through a charge controller, which regulates the flow to avoid overcharging. Your battery stores the energy, and when needed, an off-grid inverter converts the DC power from the battery into AC electricity to power your household appliances. This setup is typically the simplest and most efficient, making it ideal for smaller off-grid households such as cabins or one-bedroom homes. - AC Solar System
An AC-coupled system works slightly differently. The DC electricity from your solar panels is converted to AC by a solar inverter first. This AC power is then sent directly to your home and is used to run your electrical appliances. If there’s any excess energy, it’s then sent to a battery, with an additional inverter converting the AC power back to DC. This setup is more complex than a DC system but offers greater flexibility as it allows you to more seamlessly replace your battery. Particularly useful for larger systems or when replacing an existing grid-tied solar setup to work off-grid. - Mixed AC and DC Solar System
A hybrid system combines both your AC and DC elements. It uses a hybrid inverter, which can manage DC power from your solar panels to charge your batteries directly, while also converting DC to AC for household use. This type of system provides both the flexibility of an AC system and the efficiency of a DC system, making it suitable for modern off-grid homes with varying power demands and backup requirements.
Benefits of an Off-Grid Solar System
Choosing to install an off-grid solar system can be a great investment, due to the following benefits:
- Positive Environmental Impact
By disconnecting from the grid, you are reducing your carbon footprint. Traditional electricity is created by burning fossil fuels, which are major contributors to air pollution. By relying completely on renewable solar power, you can help mitigate the demand for grid-connected electricity to ultimately benefit the environment. - Suitable for rural areas
If you live in a rural or remote region, you may be worried about energy availability. Access to the grid may be limited, with less infrastructure in place to deliver the appropriate power to satisfy your needs. Switching to an off-grid system can be a viable solution, eliminating the need to rely solely on the grid for energy and making your property self-sustaining. - Energy Control
You’re in complete control of your power. This can be great during instances where the grid suffers a blackout, energy shortage or failure, with you unaffected because of your self-sufficient supply. - Saving money long-term
Once you disconnect from the grid, you’ll no longer have to worry about rising energy costs or looming electricity bills, as you’re generating completely free energy from the sun. This can be a great way to offset the costs of your initial investment, particularly as electricity prices increase across Tasmania.
Cons of an Off-Grid Solar System
The following drawbacks to off-grid installation could prove a challenge to Tasmanians:
- No Backup Grid Support
Using an off-grid system, you are completely disconnected from the main grid. This could prove challenging during periods when solar energy is more difficult to generate. For instance, if cloudy weather blocks out the sun, there is a chance that you will use all of your available energy. Unlike grid-connected systems, you can’t simply purchase backup electricity, with energy only available when your solar system has the chance to replenish itself. Choosing to install a backup generator or larger battery can reduce these concerns. To help avoid these shortages, at Tasmanian Safer Solar (TSS) we recommend a battery that connects directly with a backup generator, providing added reliability when solar energy isn’t available. - Higher initial costs
Installing a solar system powerful enough to run your entire home by itself will require higher upfront costs. This allows you to cover the larger capacity battery and add solar panels. Your solar battery in particular can account for 30-40% of your total cost, with a larger capacity ensuring you have all the necessary stored energy. These costs can be 50% more than being on the grid. In a grid-tied system, you can also still benefit from the Virtual Power Plant (VPP), where you receive financial compensation for exporting excess energy. Off-grid systems can also participate in a VPP, provided you have the necessary components, such as a VPP-compatible battery and an ongoing internet connection. Tasmanians can also offset the higher upfront costs by applying for government rebates, such as the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme. - Changing energy usage
To make an off-grid system viable, you may be required to make wholesale changes to your energy habits. With a limited supply of solar energy and no backup connection to the grid, you’ll need to use your power carefully. This can include prioritising your power use during the day and limiting your appliance use at night. These behavioural changes may be challenging, and it is important to consider them before making the jump.

Factors to Consider When Going Off-Grid
Before installing your off-grid system, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Energy Needs and Consumption
You must ensure your off-grid system is properly sized to meet your energy usage. Your local installer will gather this information when conducting their sizing profile. Allowing them to forecast your daily consumption, and which appliances you need to prioritise. You can begin to understand your usage by examining energy bills and pinpointing your consumption patterns, which can include: your peak demand periods during the day, and any seasonal changes. An incorrect forecast of your energy consumption can render your off-grid system useless and unable to support your daily requirements. - Sunlight Availability and Climate
Because an off-grid system is entirely dependent on solar energy, it’s important to assess your location and weather conditions. For instance, living in an area with longer daylight hours and sunnier conditions will be more appropriate for an off-grid system than overly cloudy regions. This may be an issue for parts of Tasmania where sunlight is harder to come by, particularly during winter. This doesn’t mean you can’t build an off-grid system; it just means you may need a larger battery capacity to compensate for the energy losses during cloudy days. - Choosing the Right Installer
When making the jump to off-grid, it’s essential to choose an installer you can trust with support throughout the entire process. Their support shouldn’t end with planning and installation, as their post-installation service will be essential. You are dependent on your solar all year round, which makes maintenance, repairs and troubleshooting of added importance. Choosing our knowledgeable team at Tasmanian Safer Solar (TSS) can ensure you are provided the best and most up-to-date information. We are accredited by the Clean Energy Council and are more than prepared to support you through each step of this exciting investment.
Cost of an Off-Grid Solar System
The total cost of your off-grid system will vary heavily depending on the size of your system, your personal consumption levels, your location and the quality of the installer. To provide an estimate of average costs, the guide below outlines approximate prices based on your selected size:
- Small-sized system: Typically consists of a 3-5 kW solar panel size, a 8-10 kWh capacity battery and a 3-5 kW inverter. This will be enough to power a small number of appliances, which may include a few lights, a fridge, a TV and a computer. For this size, costs will fall between $20,000 to $30,000
- Medium-sized system: Consists of 6-8 kW solar panels, 20 kWh capacity battery and a 5-10 kW inverter. It will be suitable for the average household, enough to power your everyday appliances with a mix of solar panel generation and battery storage. Costs will fall between $35,000 to $45,000.
- Larger-sized system: Consists of solar panels greater than 10 kW, 30 kWh capacity batteries and a 15-45 kW inverter. This will be enough to power a larger house with higher energy usage with costs of $50,000 to $65,000.
Leaping to an off-grid solar system can be daunting. By disconnecting yourself from backup grid power, you are putting complete faith in solar energy to power your home. This can be a great investment because it provides you with energy autonomy and resilience against power outages. However, the increased capacity comes with higher upfront costs compared to grid-connected systems, and you may need to make significant adjustments to your energy usage to ensure it operates effectively. For more information about off-grid solar systems and expert guidance in making the right choice, contact your local specialists at TSS.