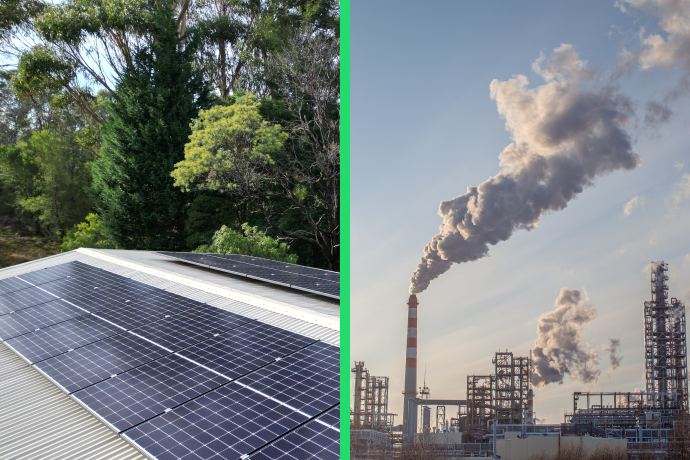
Solar panels are an energy efficient source of power compared to fossil fuels and use less energy to perform the same task. The photovoltaic panels convert sunlight into electricity as opposed to their non-renewable counterparts. To understand why solar panels are energy efficient, you need to understand the technology behind them, types of panels and how they are superior in overall efficiency compared to coal and gas.
What is Solar Panel Energy Efficiency?
Solar panel efficiency can be quantified in two different ways. The technology is energy efficient compared to fossil fuels that are contrasting sources of power. It is also energy efficient because of the capacity to convert sunlight to electricity.
Solar Panels vs Fossil Fuels
Solar panels are more energy efficient than coal or gas overall as they are renewable, require less energy for operation, and have a lower carbon footprint. Although fossil fuels convert fuel into energy at around 35 to 40% compared to solar panels at around 15 to 25%, they lose a significant amount of energy as waste and heat. By converting sunlight into electricity, solar panels require no other external source of energy and zero greenhouse gas emissions. While fossil fuel power plants may have higher instantaneous energy conversion efficiencies, other factors like greenhouse gas emissions and life cycle emissions show that solar is far more efficient in a broader environmental and economic sense.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
| Metric comparison | Solar panels | Fossil fuels |
| Instantaneous conversion efficiency (the effectiveness of converting energy from one source to another) | 15 % to 25% | 35% to 40% |
| Lifecycle CO2 emissions (total greenhouse gas emissions produced through the life cycle) | Very low. 46 gCO₂eq/kWh (median)
On average, generating 1kWh of electricity with solar panels results in the emission of 46 grams of CO2. |
Very High: 1,960 gCO₂eq/kWh (median)
By generating 1kWh of electricity, fossil fuels like coal or gas result in the emission of 1,960 grams of CO2. |
| Greenhouse gas emissions from solar panels vs fossil fuels | Solar panels have minimal greenhouse gas emissions because of the process of generating energy from sunlight | Fossil fuels have extremely high greenhouse gas emissions because of the extraction, transportation and production process. They continually produce CO2 emissions while in use. |
Solar Panel Conversion of Sunlight to Electricity
Solar panel energy efficiency also refers to how well the solar panel converts sunlight into electricity. This is quantified in a percentage to compare how efficient they are with efficiency usually ranging between 15% and 20%. A 20% energy efficient solar panel converts 20% of the sunlight that strikes the panel into electricity. Higher efficiency panels means that more sunlight is converted to electricity in a smaller space.
How is Solar Panel Energy Efficiency Measured?
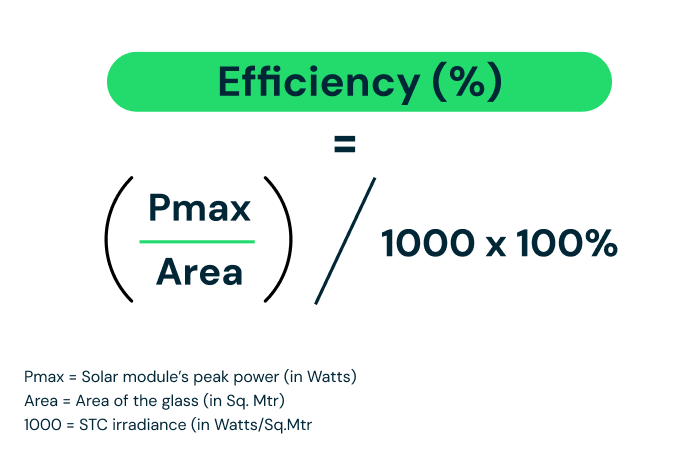
Solar panel efficiency is measured using a calculation that divides the power output of the solar panel over its surface area in standard test conditions. The calculation takes into account the power rating in kilowatts divided by the total panel area multiplied by 100 to get a percentage. When referring to ‘standard test conditions’, it is the conditions set out for testing that is based on a cell temperature of 25°C, solar irradiance of 1000W/m2 and air mass of 1.5. The overall solar panel efficiency measurement is graded by taking into account the irradiance level and cell type.
What Makes Solar Panels Energy Efficient?
To understand what makes solar panels energy efficient, we need to look at how they work. It is the photovoltaic effect from the solar cells that causes the conversion of sunlight to electricity. To ensure efficiency, the panels are made of semiconductor material like silicon that is in a metal frame and glass case. Semiconductor materials exposed to sunlight cause electrons to be released and produce an electric charge. The sunlight makes the solar panels energy efficient through this photovoltaic effect. The electrical current is captured as DC electricity within the wiring of the solar panels. An inverter then converts it to AC electricity to be used within a home or business.
Some solar panels are more energy efficient than others, meaning they convert a higher percentage of electricity from sunlight in a smaller space. High quality panels like monocrystalline and polycrystalline have an energy efficiency of 20-25% and 18-21% respectively compared to thin film panels at about 10-13%. The solar cell technology in monocrystalline solar panels with its uniform structure makes this type of panel the most highly efficient.
Other Factors that Influence Solar Panel Energy Efficiency
While the technology of solar panels and cells is the main way the solar panels are energy efficient, there are some other factors that contribute to the level of efficiency.
- Type of solar cells: The types of solar panels affect energy efficiency because of their cell composition. Monocrystalline solar panels are made up of a single crystal and have dark edges. The high purity silicon cells make them more energy efficient than other solar panels. Polycrystalline is also a highly efficient panel due to its solar cells but slightly lower than monocrystalline. These panels are made by melding together multiple silicon fragments resulting in a solar panel that is still energy efficient. Thin film solar panels, on the other hand, are the least efficient as they use thin, non-crystalline photovoltaic cells that produce much less energy from the sunlight.
- Panel design: The panel design affects the efficiency of solar panels by the cell configuration and colour of the backsheet. The way the cells are configured along the panel impacts how sunlight can connect to the solar panels. If the backsheet is blue or green it is more effective than black as it reflects, rather than absorbs the high temperatures that can reduce efficiency.
- Panel inclination: Solar panels need to be able to receive sunlight to convert it to electricity so the panel inclination is imperative. They need to be tilted towards the sun and positioned in a way to avoid any shade for maximum exposure.
- Temperature: Solar panels require sunlight to produce electricity, but do not work well in extreme temperatures. The best temperature for solar panels to operate at is 25°C. Every degree the solar panel measures above that temperature reduces efficiency. While solar panels rely on sunlight to create energy, excessive heat reduces the energy efficiency.
- Shade and cloud: Although solar panels do not need heat to generate electricity, they do need sunshine. The lower the amount of sunlight that connects to the solar cells, the less energy will be produced. For maximum energy efficiency solar panels should be placed in the least shady area with the most amount of sunlight.
- Panel age: As solar panels deteriorate over time and become less efficient, the age of the panel will impact efficiency.
- System balance: Parts like the mounting structure, cables, inverters, and protection devices all need to be well balanced to ensure maximum energy efficiency. Without the correct balance, the system will be less efficient and potentially have a shorter lifespan.
- Professional installation: It is important to use professional solar panel installers from a reputable company to ensure the best energy efficiency from your solar panels. Solar installers know how to position the panels to get maximum sunlight exposure, and the best materials to use for each solar system installation.
Do Solar Panels Lose Energy Efficiency Over Time?
Solar panels do lose energy efficiency over time and this is called panel degradation. Solar panels will remain energy efficient for decades but do lose efficiency slowly over time. This degradation is a response to the fact solar panels are exposed to the elements like UV rays and weather conditions. Most solar panels will operate at about 90% of their original capacity for at least 20 years as the degradation rate is about 0.5% loss for each year. When solar panel efficiency drops it is because of either light induced degradation, potential induced degradation or age related degradation.
- Light induced degradation (LID) happens when the solar panel is first exposed to sunlight. The solar panel efficiency is often reduced by 1 to 3% from the initial solar exposure. This cannot be avoided and happens only once during the lifespan of the solar panels.
- Voltage heat and humidity cause potential induced degradation (PID) although it may not impact all solar panels. PID causes a reduction in energy efficiency when the module voltage potential and the leakage current drive ions to move within the module and between the semiconductor material, glass or frames. By using high quality solar panels from quality suppliers, PID can be avoided or reduced.
- Solar panels naturally degrade with age. They have a lifespan of about 25 to 30 years during which they are exposed to natural wear and tear which causes energy efficiency to drop.
Solar panels are energy efficient because they use sunlight to create electricity with no harm to the environment. Compared to fossil fuels like coal and gas, they also have the highest energy efficiency rating. While the energy efficiency may decline over time, it is still 90% of the original solar panel rating after 20 years. To find out more about energy efficiency of solar panels, contact the team at Tasmania Safer Solar.