An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) electricity to alternating current (AC) electricity to be used to run household appliances and electronics. Converting DC to AC allows sources like solar panels, generators and batteries to power household equipment, portable electronics and off-grid power systems. The appliances in the home are designed to run off an AC supply which they get from electric outlets which all provide AC electricity. Solar panels and batteries produce DC electricity so, if we want to power our electrical devices from renewable sources, battery banks or even a car, it needs to be converted from DCelectricity to AC electricity with an inverter. A regular inverter converts DC electricity from a battery, car, generator, or off-grid system into AC that a home can use, while a solar inverter converts the DC electricity produced by solar panels.
How Does an Inverter Work?
An inverter works by using sophisticated electronics and circuitry to convert the DC power source to a usable AC power source. The DC power enters the inverter where electronic switches turn the power on and off rapidly. The switch of direction needs to happen 50 to 60 times within a second which is impossible by human hand, so an automated device needs to be used. By switching the DC current back and forth from the on and off position, the inverter is able to create a synthetic AC waveform. Inverters can have different designs depending on the application it is being used for, power capacity, and the chosen technology.
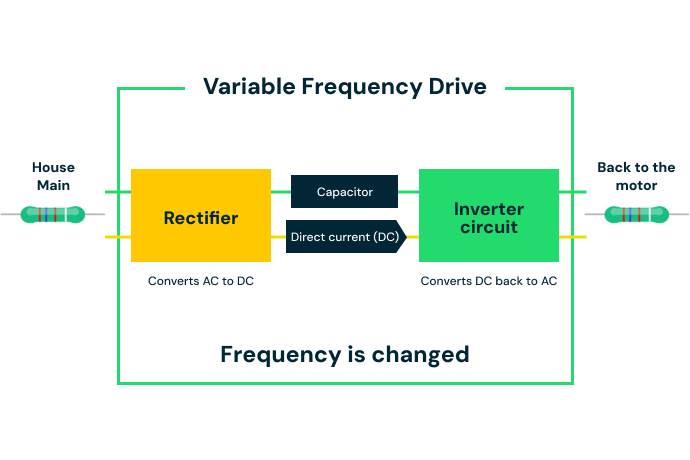
Applications for Inverters
Inverters are used for a variety of applications when DC electricity needs to be converted to AC for power. The most common applications for inverters include:
Solar power
For a solar system to work and supply electricity to a home, it must have a solar inverter. An inverter is one of the most important pieces of equipment in the solar system. Solar panels and other photovoltaic systems produce DC electricity by harnessing the sun’s energy through the photovoltaic effect. Homes and businesses, however, use AC electricity to power appliances and lights. The standard on-grid solar power system uses a solar inverter to convert the DC electricity to AC to be used in the home or sent back to the grid.
A solar inverter has transistors and electronic switches inside to convert the DC electricity to AC electricity. These transistors switch on and off quickly at around 3000 times a minute which creates the AC waveform. The inverter synchronises the AC output to ensure that the solar electricity generated can be seamlessly integrated with the existing power supply. It is then able to be sent to the electrical grid of the home and distributed to electrical appliances.
There are different types of solar inverters for different needs. These include string inverters, microinverters and hybrid inverters.
- String inverters: This is the most common type of solar inverter because it connects a series of solar panels together. The panels in a string are connected by their positive and negative terminals, creating a single path for the electric current which connects to a central unit. These inverters are the most cost effective due to their simple design. They are low maintenance, highly efficient and easy to install.
- Microinverters: Rather than having one central solar inverter, this system has a microinverter on each individual solar panel. This type of inverter is ideal for shaded areas because you only lose output from one or two panels that are in the shade, rather than the whole solar panel array. These inverters are particularly safe as there is direct DC to AC conversion on each panel, eliminating the need for high voltage wiring.
- Hybrid inverters: These are advanced inverters that convert DC electricity to AC electricity for solar panels and batteries. Battery inverters convert DC power from the battery into AC power, while solar inverters convert this energy derived from the solar panels.
Home backup batteries
If you want backup power, but your home is not suitable for a solar system, a home backup battery is the next best option. This system charges from the electrical grid or a generator to provide backup power during outages. It also creates DC electricity and needs an inverter to form usable AC power. To convert the power, a home backup battery has a couple of inverter options. Some batteries have built-in inverters where they can charge from the grid and use the built in inverter to convert to DC power. Hybrid inverters can also be used for home backup batteries without solar, provided the inverter is compatible with the grid charging with the proper configuration.
Electric vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) need inverters to convert the DC current to AC power to run the motor vehicle. Without an inverter, the vehicle would not be able to function. The EV inverter takes the DC power from the high voltage battery and converts it to AC power. It also regulates the frequency and voltage of AC power that is delivered to the vehicle. The best types of inverters for EVs are three-phase inverters for high performance vehicles and single-phase for smaller less demanding cars.
Difference Between an Inverter and Solar Inverter
The two main types of inverters are solar and general inverters. While they both perform the same function of converting DC electricity to AC, they have several differences. Solar inverters work with solar panels, taking the DC power made by the panels and turning it into AC power for the home. General inverters used in backup power systems change the DC power from batteries into AC power. However, they lack the solar specific optimisation features.
The main differences between an inverter and solar inverter are:
Primary function
- A solar inverter converts DC electricity specifically from solar panels to AC electricity to be used in the home.
- A general inverter converts DC electricity to AC from batteries, generators or other off-grid systems.
Power source
- A solar inverter uses the photovoltaic effect of solar panels to create DC power. This includes maximum power point tracking (MMPT) to maximise the energy captured by the solar panels.
- A general inverter uses a variety of sources including batteries and home backup power to generate DC power. They do not have the MMPT ability.
Suitability for environments
- A solar inverter is designed for outdoor exposure with weather resistant and temperature stability features. They are built to withstand harsh conditions like dust, storms, water and extreme temperatures
- A general inverter is designed to be installed indoors or protected from the elements. They require a cool, well ventilated area to prevent overheating.
Climate requirements
- A solar inverter works best in sunny areas. They require homes that receive a certain amount of sunshine per day to produce solar energy.
- A general inverter can work in any climate and do not require a special setup like solar panels to operate.
Cost implications
- A solar inverter costs more than a general inverter and can often be about 30% of a solar system setup cost. They do save money in the long run with reduced reliance on the grid.`
- A general inverter is usually less expensive to buy at first but will not save you any money on electricity bills.
Grid interaction
- A solar inverter can be grid tied which means it can send excess electricity back to the grid to earn credits. It is also designed to shut down safely during a power outage to prevent backfeeding to the grid.
- A general inverter cannot feed power back into the utility grid as its only function is to convert DC to AC electricity.
Monitoring
- A solar inverter often has advanced features like built-in monitoring to track power production, identify faults and report system performance.
- A general inverter has a more straightforward function without the additional features of advanced monitoring capabilities.
Why is it Important to Know What an Inverter is?
It is important to have knowledge about inverters as they are responsible for converting the direct current to usable electricity in a variety of applications. Whether you are looking for a sustainable energy resource, or wanting mobile or home backup power, choosing the right inverter is essential. The key reasons to understand inverters include:
- Ensuring compatibility: Most importantly, the inverter you choose must be compatible with your system. A solar system will require a specific solar inverter to operate effectively. Standard inverters are not compatible with solar panels.
- Preventing damage and ensuring safety: Choosing the right inverter will prevent damage and ensure safety by matching power capacity to needs. The right inverter will have the built in protection features the system needs to function properly. Incompatible inverters can lead to electrical faults, overheating, short circuits or wiring problems.
Inverters are devices that convert DC electricity to AC electricity to be used for powering household appliances, off grid living, home and mobile backup power. Without an inverter, energy received from sources like solar panels, batteries or generators cannot be used in the home, caravan or businesses. An inverter is one of the most important parts of a solar system. To find out the best type of inverter for your home, contact the team at Tasmania Safer Solar.






